Matchless Tips About How To Treat And Prevent Boils

When it is advanced, a boil can disappear on its own or increase in size.
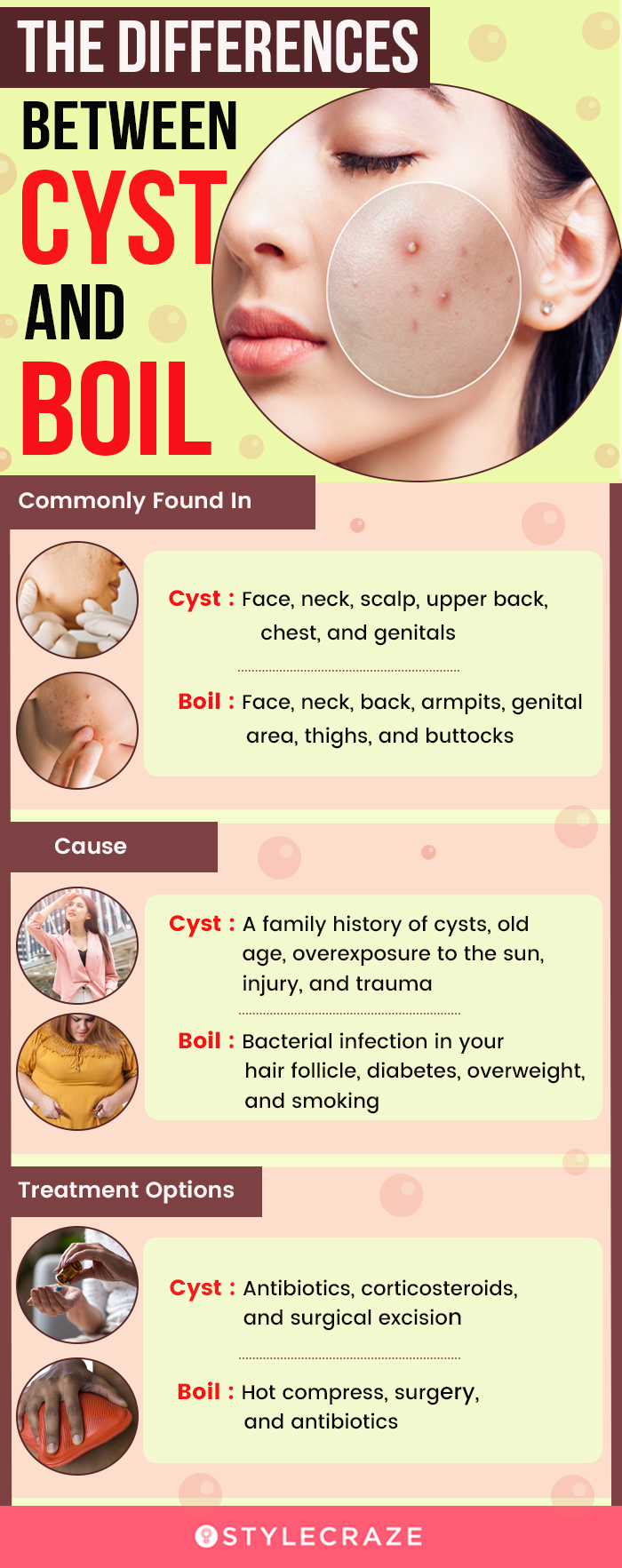
How to treat and prevent boils. Follow these tips to prevent the development of boils and their spread: When you have a boil, washing and keeping your clothes and bedding clean can also help prevent the. Common antibiotics used to treat boils include dicloxacillin, cephalexin, and clindamycin.
However, you can prevent a boil from spreading to other parts of your body by following these tips: They usually go away on their own, but. These include applying raw onion, garlic juice, turmeric paste, or goatweed essential oil to the boil.
In this article, we’ll discuss how to treat boils at home, what causes them, the signs and symptoms of boils, and how to know when to seek medical care for a boil. Keep your razors clean and sharp.
As with any infection, you should keep the area clean. It will also provide information on how to treat a skin boil and when you should call a healthcare provider. It is best to steer clear of such public utilities as you run the risk of spreading the infection to others.
For larger boils and carbuncles, treatment may include: The staph bacteria that causes boils can be spread by sharing personal items such as razors. You can take the following steps at home to encourage the boil to drain and relieve your pain:
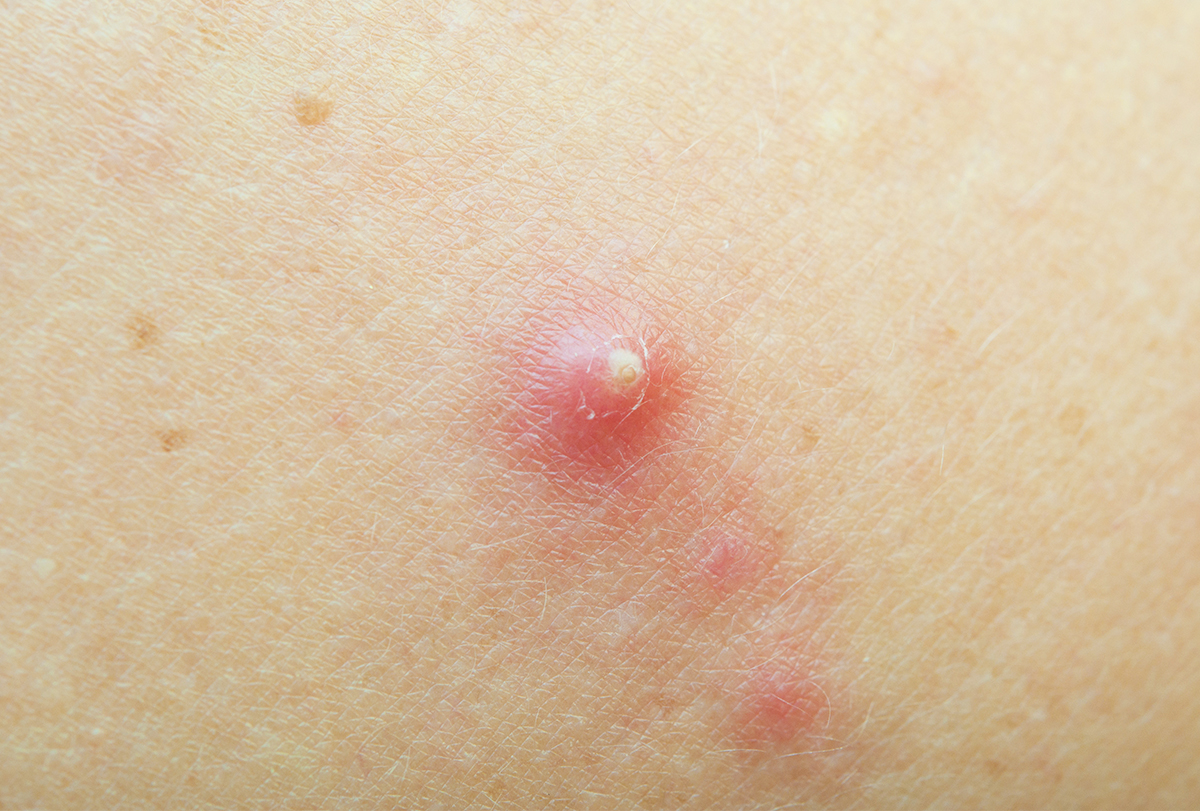
Is that a boil you’re seeing? Shaving to avoid boils 1. Carbuncles are clusters of several boils.
Make sure your warm compress is not too hot (test it on the skin of the back of your hand) to avoid causing a scald or burn. Follow these tips: Overview what are boils and carbuncles?
Boils are usually caused by the bacteria staphylococcus aureus ( staph infection ). Topical antibiotics, such as mupirocin or neomycin, can help to prevent the spread of bacteria and promote faster healing. A carbuncle is a cluster of boils that form a connected area of infection under the skin.
* keep the boil covered with a clean bandage at all times. You can reheat the compress and apply again for 5 minutes, repeating for a total of 20 to 30 minutes. When they increase in size they become abscesses and are of significant concern, both medically and cosmetically.
In this phase, doctors usually recommend applying a warm, moist, antiseptic compress (a cloth pad held in place by a bandage) or a special ointment that draws (pulls) pus out of the boil. They can start as small, red bumps and turn into hard lumps under your skin that secrete pus. Wet a cloth with warm water.